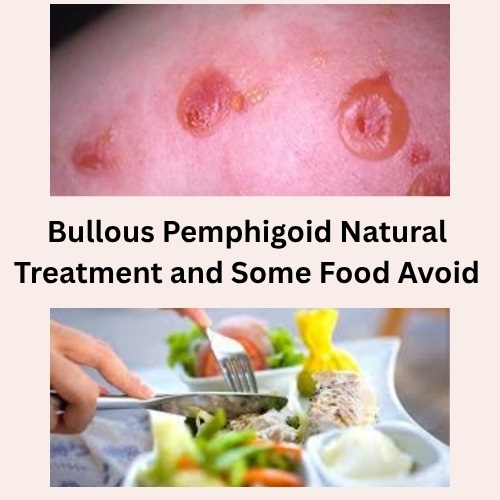
Bullous Pemphigoid is a kind of chronic skin disorder connected with the outbreak of tense blisters on the skin surface. The blisters are large and fluid filled that normally appears on the areas that often flex, such as armpits, arms, lower abdomen and legs.
Bullous Pemphigoid happen when your immune system attacks a thin layer of tissue below your outer layer of skin. The cause for this abnormal immune cause is unknown, though it sometimes can be triggered by taking certain medications.
Bullous Pemphigoid Symptoms
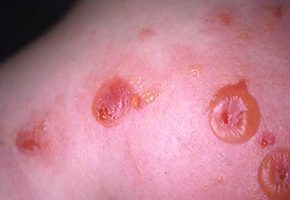
The major characteristic of bullous pemphigoid is the appearance of fat blisters that don’t easily rupture when touched. The fluid inside the blisters is usually clear but may contain some blood. The skin approximately the blisters may appear normal, reddish or darker than normal. Various people with bullous pemphigoid grow an eczema or hive like rash rather than blisters.
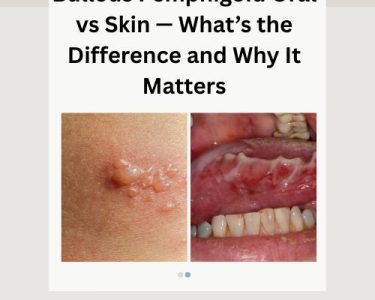
Acute itching, inflammation, skin rashes, mouth sores and bleeding gums are some of the Symptoms of Bullous Pemphigoid.
Multiple blisters or bullaes appearing with elevation of the skin filled with serous liquid can be found in severe cases. Such bullous pemphigoid blisters generally affect the arms, legs and middle part of the body. Blisters in many people with bullous pemphigoid also grow in the mouth. When blisters break open, they lead to formation of ulcers.
Related Articles: 8 Natural Remedies for Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous Pemphigoid Causes
Although the exact Causes of Bullous Pemphigoid are not well unstated, it is believed these blisters occur because of a malfunction in your immune system. Human immune system release antibodies to fight foreign bodies like viruses, bacteria, etc. For reasons that are not clear, the body may grow an antibody to a exacting tissue in your body.
When these antibodies connect the epidermis and the next layer of skin, these trigger inflammations which create the blisters and itching of bullous pemphigoid.
How to Treat Bullous Pemphigoid
If you’re searching for how to treat bullous pemphigoid, you’re likely dealing with painful blisters and irritated skin caused by this autoimmune condition. Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation, relieving symptoms, and preventing flare-ups. The most common medical approach includes corticosteroids (such as prednisone), either topical or oral, along with immunosuppressants to control the overactive immune response. Antihistamines may also be used to ease itching and discomfort.
In addition to medications, lifestyle and dietary changes can support the healing process. Following a bullous pemphigoid treatment diet—low in inflammatory foods—may help minimize symptoms. This includes eating antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables, omega-3 fatty acids (like in flaxseeds or fish), and avoiding processed foods, sugar, and potential allergens like gluten or dairy.
Proper wound care is essential: keep blisters clean and dry, use non-stick bandages, and avoid skin trauma. Regular follow-ups with a dermatologist are crucial to monitor progress and adjust treatment as needed.
Ultimately, understanding how to treat bullous pemphigoid involves a combination of medical therapies and supportive dietary measures to reduce flare-ups and promote skin healing. Always consult with a healthcare provider before making any treatment or dietary changes.
Bullous Pemphigoid Natural Treatment
Bullous pemphigoid is a rare autoimmune skin disorder that causes large, fluid-filled blisters on the skin. While conventional treatments often involve corticosteroids and immunosuppressants, many people are exploring bullous pemphigoid natural treatment options to reduce symptoms and improve skin health without harsh side effects.
Natural remedies may help support the immune system and soothe inflammation. Aloe vera gel, for example, is known for its cooling and anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce itching and discomfort when applied topically. Turmeric, a powerful anti-inflammatory herb, may also be beneficial when taken as a supplement or added to meals. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in flaxseed and fish oil, are another excellent option to support immune function and skin repair.
Although bullous pemphigoid and pemphigus vulgaris are different autoimmune conditions, some natural treatment for pemphigus vulgaris approaches may overlap. These include a nutrient-rich anti-inflammatory diet, stress management techniques like meditation, and the use of herbal supplements such as ashwagandha or licorice root under medical supervision.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any natural therapy, especially when dealing with autoimmune diseases. Combining traditional medicine with natural support may offer a more balanced and gentle path to healing.
1. Aloe Vera for Skin Healing and Soothing
Aloe vera is widely recognized for its soothing and anti-inflammatory properties. When applied topically, aloe vera gel can help reduce itching, irritation, and redness associated with BP. It also accelerates the healing of blisters and wounds, promoting skin regeneration. Aloe vera can be used as a natural remedy in addition to medical treatments, providing symptomatic relief from the discomfort caused by BP.
How to Use:
- Apply fresh aloe vera gel directly to the affected areas.
- Leave it on for about 15-20 minutes, then rinse with lukewarm water.
- Repeat this process 2-3 times a day for relief.
2. Turmeric for Anti-Inflammatory Benefits
Turmeric, particularly its active compound curcumin, is renowned for its potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Studies have suggested that curcumin may help modulate the immune system and reduce inflammation, making it a valuable natural remedy for autoimmune conditions like bullous pemphigoid.
Related Articles: Bullous Pemphigoid Natural Treatment and Some Food Avoid
How to Use:
- Mix turmeric powder with honey or coconut oil to form a paste, and apply it gently to the affected areas.
- Alternatively, you can take turmeric supplements (with a physician’s approval) or add turmeric to your diet by incorporating it into teas, curries, and smoothies.
3. Coconut Oil for Skin Moisture and Protection
Coconut oil is another natural remedy that may help in managing BP symptoms. It is rich in medium-chain fatty acids, which provide moisturizing and healing benefits to the skin. Coconut oil also has antimicrobial properties, which can be useful in preventing infections in open blisters or wounds.
How to Use:
- Apply organic, cold-pressed coconut oil to the affected areas once or twice a day to keep the skin hydrated.
- For additional relief, consider adding a few drops of tea tree oil (known for its antimicrobial properties) to the coconut oil.
4. Dietary Changes to Support Immune Health
A healthy diet plays a crucial role in managing autoimmune conditions, including bullous pemphigoid. By reducing inflammation and supporting the immune system, certain foods can help mitigate BP flare-ups. Focus on a diet rich in:
Related Articles: Bullous Pemphigoid – Autoimmune Skin Disorder
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, omega-3s have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Antioxidant-rich foods: Berries, leafy greens, and citrus fruits can help protect the skin from oxidative stress and reduce inflammation.
- Probiotics: Foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables can help promote gut health and may positively influence the immune system.
Foods to Avoid:
- Processed and sugary foods, which can trigger inflammation and worsen skin conditions.
- Gluten and dairy, which some people with autoimmune conditions find may exacerbate their symptoms.
5. Topical Calendula for Skin Healing
Calendula (marigold) is a herb known for its healing properties, particularly in treating skin conditions. It has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects, which may help with skin irritation, blisters, and healing in individuals with bullous pemphigoid.
How to Use:
- Use calendula ointment or cream and apply it to the affected areas 2-3 times a day.
- Alternatively, make a mild calendula tea and apply it to the skin using a clean cloth.
6. Manuka Honey for Healing and Infection Prevention
Manuka honey is a type of honey known for its powerful antimicrobial properties. It can help prevent infections in open blisters and accelerate the healing process. Additionally, it has soothing properties that can reduce the itching and irritation associated with BP.
How to Use:
- Apply a thin layer of manuka honey to the affected skin areas.
- Cover it with a sterile bandage to prevent it from being wiped away.
- Leave it on for several hours or overnight and rinse gently with lukewarm water.
7. Epsom Salt Baths for Pain Relief and Skin Care
Taking an Epsom salt bath can provide relief from the pain, itching, and discomfort associated with BP. The magnesium in Epsom salts can help reduce inflammation and relax the muscles, while the soothing effect of warm water can ease skin irritation.
Related Articles: Bullous Pemphigoid vs Pemphigus Vulgaris: Treatment Options You Need to Know
How to Use:
- Add 1-2 cups of Epsom salt to a warm bath.
- Soak for 15-20 minutes, ensuring that the affected areas are submerged.
- Dry off gently with a soft towel and apply a moisturizer to keep the skin hydrated.
8. Essential Oils for Skin Soothing
Certain essential oils, such as lavender, chamomile, and tea tree oil, have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. These oils can be diluted and applied to the skin to soothe irritation and support the healing process.
How to Use:
- Mix a few drops of essential oil with a carrier oil like coconut oil or jojoba oil.
- Gently massage the mixture onto the affected areas.
- Be sure to patch-test any essential oil on a small skin area first to check for sensitivities.
Foods to Avoid with Bullous Pemphigoid
When managing autoimmune skin conditions, diet plays an important role in controlling flare-ups and easing symptoms. Understanding foods to avoid with bullous pemphigoid can help reduce inflammation and discomfort caused by blistering. Certain foods may worsen the immune response and increase skin irritation, making it essential for patients to identify and avoid these dietary triggers.

Among the common foods to avoid with bullous pemphigoid are processed foods high in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats, as they promote inflammation. Acidic foods like citrus fruits, tomatoes, and spicy meals can sometimes irritate the skin and worsen blistering. Additionally, gluten and dairy products may trigger immune reactions in sensitive individuals, leading many patients to explore elimination diets for better symptom management.
It’s also helpful to compare dietary triggers with similar conditions. For instance, the list of foods to avoid with pemphigus vulgaris often overlaps with bullous pemphigoid since both are autoimmune blistering diseases. Foods containing high levels of thiols and tannins, such as garlic, onions, and tea, may aggravate symptoms in some patients. Avoiding alcohol is also recommended, as it can increase inflammation and weaken the immune system.
If you are wondering what foods trigger bullous pemphigoid, the answer varies for each person, but common culprits include gluten, processed meats, dairy, and overly spicy foods. Keeping a food diary can help identify personal triggers and make dietary changes more effective. By avoiding these problem foods and focusing on a nutrient-rich diet full of fresh vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, patients can support their overall health and potentially reduce flare-ups.
Foods that Contain Tannins
Tannins can be found in a extensive range of foods as well as beverages. People suffering from the Bullous Pemphigoid should avoid fruits and vegetables like:
- Apples
- Eggplant
- Raspberries
- Bananas
- Cherries
- Blackberries
- Avocadoes
- Pear
- Grape skin
- Mangoes
- Cranberries
- Persimmons
Some of the other general Bullous Pemphigoid foods to be keep away from, because of high tannins content include:
- Arrowroot
- Black walnuts
- Coffee
- Cumin
- Ginger
- Garlic
- Black pepper
- Cocoa seeds
- Certain varieties of tea
- Coriander
- Ginseng
- Soft drinks
- Yucca
- Kola nuts
- Rosemary
- Alcoholic beverages like wine and beer

Foods that contain Isothiocyanates
There are some different vegetables that have isothiocyanates and so cause an occurrence in people with the Bullous Pemphigoid. Given below are various of the foods that are high in isothiocyanates and must avoided:
- Cauliflower
- Broccoli
- Mustard and Mustard oil
- Turnip
- Cabbage
- Winter cress
- Radish and horseradish
- Brussels sprouts
- Seasoned sauces that contain mustard oil for flavoring
Foods that contain Thiols
Those foods that are high in thiols have been known to trigger off an outbreak of Bullous Pemphigoid in people. There are some of the common Bullous Pemphigoid food triggers containing thiols:
- Leeks
- Shallots
- Chives
- Garlic
- Onions
Foods that contain Phenols
Phenols are mostly found in the form of cinnamic acid, in lots of different food items, such as:
- Ice cream
- Beverages
- Baked goods
- Sauces and condiments
- Candy
- Fruit juice
There are some other foods too, that are high in phenols, which include:
- Black pepper
- Potatoes
- Bananas
- Mangoes
- Tomatoes
- Milk and other dairy products
It is also necessary to avoid fried food, oily or greasy food, caffeinated beverages, any form of sugar, alcohol, soft drinks, salty food, hot spices, dairy products, refined food, and so on.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
If you have bullous pemphigoid, you can help and get rid of your situation with the following self-care strategy variety of Herbal Treatment for Bullous Pemphigoid can also be very effective.
Keep Your Diet Better
If bullous pemphigoid blisters grow in your mouth, stay away from eating hard and chewable food. Do not eat food like chips, fruits and even veggies as you might feel painful to eat chew and swallow them.
Avoid Sun Exposure
Avoid prolonged sun exposure on every area of the skin affected by bullous pemphigoid.
Avoid Injury
The blisters of bullous pemphigoid and corticosteroid ointment can make your skin weak. If a blister on your skin breaks, cover it with a dry, germ-free dressing to protect it from infection as it heals.
Take Necessary Supplements
Utilization of medicine like oral corticosteroids for more than 30 days can cause problems like osteoporosis. In order to stop such situation, you must discuss with your doctor if you need calcium and vitamin D supplements.