Peripheral neuropathy is a complex, often debilitating condition that affects millions of people around the world. It develops when the peripheral nerves—those responsible for carrying vital messages between the brain, spinal cord, and the rest of the body—become injured or dysfunctional. These nerves play a crucial role in every movement and sensation we experience, which is why damage to them can trigger a wide range of troubling symptoms. Individuals may notice persistent numbness, pins-and-needles sensations, burning or electric-like pain, muscle weakness, or difficulty maintaining balance and coordination. For some, the symptoms begin gradually and worsen over time, while for others the onset can be sudden and intensely painful.
Because these symptoms can severely affect daily life, many people immediately search for fast relief or quick fixes online, often encountering claims such as say goodbye to peripheral neuropathy pain. While the desire for immediate improvement is completely understandable, truly addressing peripheral neuropathy requires first understanding what the condition is, why it develops, and how the underlying nerve damage progresses. A clear understanding of the disease provides the foundation for determining whether the nerve damage is temporary, reversible, or in some cases, permanent.
Understanding Peripheral Neuropathy
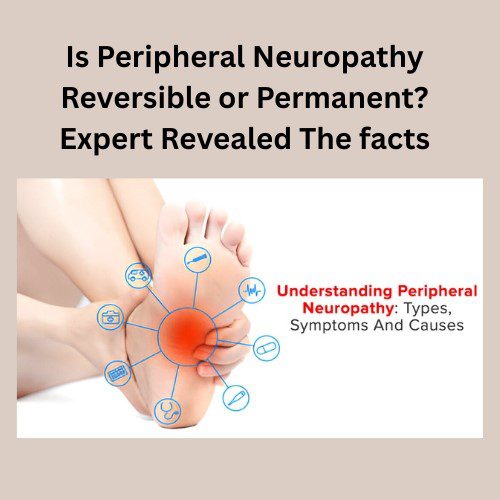
Peripheral neuropathy refers to any condition that damages the peripheral nerves. These nerves connect the central nervous system to the limbs, skin, organs, and muscles. When they are injured, the body’s ability to sense and respond properly is affected.
There are three major types of nerves involved:
- Sensory nerves – responsible for touch, temperature, and pain sensations.
- Motor nerves – control muscle movement.
- Autonomic nerves – regulate involuntary functions like heart rate, sweating, and digestion.
Damage to any of these nerve types can cause unique symptoms, but sensory nerve damage is the most common.
Major Causes of Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is not a single disease. Instead, it is a group of conditions triggered by various underlying factors. Understanding these causes is crucial because whether neuropathy is reversible depends heavily on what caused it.
Diabetes
Diabetes is the leading cause of peripheral neuropathy globally. High blood sugar damages nerves over time and reduces blood flow to nerve tissues. This connection is so common that people frequently look up terms like peripheral neuropathy and diabetes to understand why nerve pain often accompanies long-term diabetes.
Alcohol Abuse
Chronic alcoholism deprives the body of essential nutrients, especially B-vitamins, which are vital for nerve function. Alcohol also directly damages nerve tissue.
Drug-Induced Neuropathy
Some medications—especially chemotherapy drugs, certain antibiotics, and heart medications—can cause nerve damage as a side effect.
Traumatic Injuries
Accidents, falls, sports injuries, and surgeries can physically injure nerves, leading to peripheral neuropathy traumatic nervous injury.
Vitamin Deficiencies
Low levels of B1, B6, B12, and vitamin E contribute to nerve degeneration.
Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases
Conditions such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Guillain-Barré syndrome can attack nerve tissues.
Infections
Viral and bacterial infections like shingles, HIV, hepatitis, and Lyme disease can trigger neuropathy.
Genetic Disorders
Inherited neuropathies such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease affect nerve integrity from birth. Understanding the exact cause is the first step toward answering whether nerve damage can be reversed.
Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy
Symptoms vary depending on which nerves are affected, but the common signs include:
- Tingling or “pins and needles” sensations
- Burning or sharp electric pain
- Muscle weakness
- Numbness in hands or feet
- Sensitivity to touch or temperature
- Loss of coordination
- Cramping or twitching
- Reduced reflexes
- Difficulty walking
- Digestive issues (when autonomic nerves are affected)
These symptoms often start in the toes or fingertips—where nerves are longest—leading many people to search for information about peripheral neuropathy in hands and fingers when these sensations begin.
Is Peripheral Neuropathy Reversible or Permanent?
The most important question people have is: is peripheral neuropathy reversible?
The truth is that the answer depends on several factors:
- The cause of neuropathy
- How early it is diagnosed
- The extent of nerve damage
- Treatment strategies
- Patient’s overall health
Nerves do have the ability to heal—but slowly. Peripheral nerves regenerate at approximately 1 millimeter per day, meaning recovery can take months or years. Some forms of neuropathy are fully reversible, others partially reversible, and some unfortunately become permanent.
Is Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Reversible?
Diabetic neuropathy is one of the most widespread forms. Many ask: is diabetic peripheral neuropathy reversible?
- Early-stage diabetic neuropathy can be improved if blood sugar levels are strictly controlled.
- Advanced neuropathy, where nerves are severely damaged, is more difficult to reverse.
Studies show that lowering blood sugar consistently can stop nerve damage from progressing and sometimes allow partial healing. Lifestyle changes, a nutritious diet, medical treatment, and supplements can support nerve repair. However, complete reversal is not always possible, especially when nerve loss has been long-standing. The key is early detection and aggressive management.
Is Drug-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Reversible?
Another common concern is: is drug induced peripheral neuropathy reversible?
Yes—often it is, depending on the medication and the duration of exposure.
- Neuropathy caused by chemotherapy is sometimes temporary and improves gradually after treatment ends.
- Neuropathy from antibiotics or heart medications usually subsides once the drug is discontinued.
- In cases where medication permanently injures nerves, full recovery may not occur.
Working closely with a physician to adjust or change medications is essential.
Can Alcoholic Peripheral Neuropathy Be Reversed?
Many wonder: can alcoholic peripheral neuropathy be reversed?
The answer is yes, partially or fully, if:
- Alcohol use is stopped completely
- Nutritional deficiencies are corrected
- The patient adopts a healthy lifestyle
Early-stage alcoholic neuropathy can often improve significantly. However, long-term alcoholism may cause permanent nerve damage that cannot fully heal.
When Is Peripheral Neuropathy Permanent?
Peripheral neuropathy may become permanent when:
- The underlying cause is not treated for a long time
- Nerves undergo severe structural damage
- Diseases like advanced diabetes or autoimmune conditions continue to harm nerve tissues
- Physical trauma completely destroys nerve endings
Chronic cases where nerves have died completely cannot be reversed because dead nerves cannot regenerate. But even when neuropathy is permanent, treatments can reduce pain, improve mobility, and enhance quality of life.
Diagnosing Peripheral Neuropathy
A proper diagnosis determines the cause and extent of nerve damage. Doctors may perform:
- Blood tests
- Nerve conduction studies
- Electromyography (EMG)
- Imaging scans
- Nerve biopsy
- Vitamin level testing
- Glucose testing for diabetes
Accurate diagnosis is essential to determining recovery potential.
Can Peripheral Neuropathy Improve Naturally?
Many people look for alternative ways to manage neuropathy. In fact, some consult holistic approaches like natural supplements for peripheral neuropathy, hoping to enhance nerve repair. While natural methods cannot replace medical treatment, they can support nerve health when used appropriately.
Effective Ways to Support Nerve Recovery
Although there is no single cure for neuropathy, several approaches can significantly improve symptoms and support nerve healing.
Controlling Underlying Conditions
Managing diabetes, autoimmune diseases, infections, and vitamin deficiencies is the cornerstone of neuropathy treatment.
Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals strengthens nerve function.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Regular movement increases blood flow to nerves and restores muscle strength.
Medications
Pain relievers, anticonvulsants, antidepressants, and topical treatments may help reduce symptoms.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Stopping alcohol, quitting smoking, managing stress, and adopting healthy habits boost nerve repair.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outlook
Peripheral neuropathy outcomes vary widely. With early diagnosis, lifestyle changes, medical treatment, and consistent management, many people experience major improvements. Some even achieve full recovery when nerve damage is caught early and addressed properly.
In severe or advanced cases, treatment focuses on symptom relief and preventing further nerve deterioration. Even then, quality of life can be significantly improved with proper management.
Home Remedies and Natural Approaches
Many people search for gentle, home-based solutions such as effective ways to recovery of peripheral neuropathy with home remedies, which can complement medical treatment and support long-term nerve regeneration.
Warm Foot Soaks
Improves circulation and reduces stiffness.
Massage Therapy
Relieves tension and stimulates nerve endings.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Reduces pain and inflammation in affected areas.
Herbal Solutions
Some individuals explore treatment for peripheral neuropathy by natural herbal remedies to complement traditional therapies, especially for mild symptoms.
Vitamins and Supplements
B-complex vitamins, alpha-lipoic acid, magnesium, and omega-3 fatty acids are associated with improved nerve function and are often part of natural treatments for peripheral neuropathy with supplements and vitamins for those seeking alternative support.
Conclusion
Peripheral neuropathy is a challenging condition, but the key to answering is peripheral neuropathy reversible lies in understanding the cause, severity, and timely intervention. Some forms—especially those related to diabetes, medications, and alcohol—can be reversed or significantly improved when treated early. Others may become permanent if diagnosis and treatment are delayed.
Whether the condition is reversible or not, modern medical care, lifestyle changes, supplements, and supportive therapies can dramatically reduce symptoms and help patients regain control of their daily lives. With the right knowledge and proactive management, individuals can slow the progression of neuropathy and, in many cases, achieve meaningful recovery and relief.