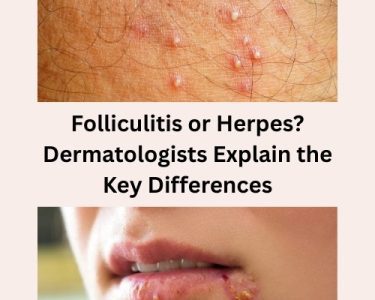
Folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicles, often resulting in red, itchy, and sometimes painful bumps on the scalp. While it is generally harmless, folliculitis post hair transplant can cause discomfort and anxiety, especially for individuals concerned about the success of their hair restoration. Understanding this condition, including its causes and symptoms, is essential for effective management and proper recovery.
Hair transplant procedures have become increasingly popular for those seeking a permanent solution to hair loss. However, like any surgical procedure, hair transplantation carries potential risks and complications. One of the most common concerns after surgery is the development of folliculitis around the newly implanted follicles.
Interestingly, some patients initially confuse folliculitis or herpes? when they notice these bumps for the first time. While both conditions can cause irritation and redness, their underlying causes and treatments are very different. Recognizing the distinctions early helps prevent unnecessary panic and ensures timely care.
What Is Folliculitis?
Folliculitis is a common skin condition characterized by inflammation of the hair follicles. It usually appears as red, itchy, or pus-filled bumps around the hair follicles. While it can occur anywhere on the body where hair grows, it is most common on the scalp, face, neck, chest, back, and legs.
Causes of Folliculitis
- Bacterial Infection: Most commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
- Fungal Infection: Yeast or other fungi can infect hair follicles.
- Irritation: Shaving, tight clothing, or friction can trigger folliculitis.
- Blocked Follicles: Sweat, oils, and dead skin cells may block follicles.
Symptoms of Folliculitis
- Small red or white bumps around hair follicles
- Itching or tenderness
- Pus-filled blisters that may crust over
- Mild burning or discomfort
Types of Folliculitis
- Superficial Folliculitis: Affects the upper part of the hair follicle.
- Deep Folliculitis: Involves the entire hair follicle and may cause larger, painful bumps.
Treatment and Care
- Keep the area clean and dry
- Avoid shaving or irritating the affected area
- Topical antibiotics or antifungal creams may be prescribed
- Severe cases may require oral medications
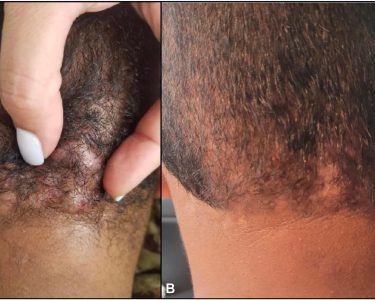
What is Folliculitis Post Hair Transplant?
Folliculitis post hair transplant refers to the inflammation or infection of hair follicles following a hair restoration procedure. During transplantation, tiny incisions are made in the scalp to implant hair grafts. This creates a vulnerable environment for bacteria, fungi, or other irritants to enter the follicles, triggering inflammation.
Post-transplant folliculitis can appear as small red bumps, pustules, or even cyst-like formations. It is usually localized to the areas where the hair grafts were implanted but can occasionally spread if not addressed promptly. While mild cases often resolve on their own, severe cases may require medical attention.
Patients may also notice discomfort similar to Folliculitis – Hot Tub Rash And Inflammation, a condition where folliculitis occurs after exposure to contaminated water. This analogy helps illustrate the mechanism of infection and inflammation.
Causes of Folliculitis Post Hair Transplant
Understanding the causes of post hair transplant folliculitis can help patients prevent complications and manage symptoms effectively. The main causes include:
Bacterial Infection
The most common cause is bacterial infection, often by Staphylococcus aureus. This bacterium can enter the scalp during or after the transplantation procedure, leading to inflammation of the newly implanted follicles.
Blocked Hair Follicles
Hair follicles can become blocked by oil, dead skin cells, or external debris, causing irritation. After a hair transplant, these follicles are particularly sensitive, making them more prone to developing folliculitis.
Poor Post-Operative Hygiene
Neglecting proper scalp hygiene after the procedure can increase the risk of infection. Sweat, dirt, or unclean hands touching the transplanted area can trigger severe folliculitis post hair transplantation.
Immune System Response
Some patients may experience an inflammatory response from their immune system as it reacts to the newly implanted hair follicles. While this is a natural healing process, excessive inflammation can mimic or worsen folliculitis symptoms.
Use of Occlusive Hair Products
Heavy hair products, such as oils, gels, or creams, can trap bacteria in the follicles. This can exacerbate inflammation and increase the risk of developing folliculitis after hair transplantation. Folliculitis can also appear in specific forms which shows how environmental exposure can sometimes trigger outbreaks.
Symptoms of Folliculitis Post Hair Transplant
The symptoms of folliculitis post hair transplant can range from mild to severe. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for timely treatment.
Red Bumps Around Hair Follicles
One of the earliest signs is the appearance of small red or pink bumps around the transplanted follicles. These bumps may resemble pimples and can sometimes contain pus.
Itching or Burning Sensation
Patients often report itching or a mild burning sensation in the affected area. Scratching can worsen inflammation and potentially lead to scarring.
Pain or Tenderness
In some cases, the affected follicles may be painful to touch. Pain is often associated with severe folliculitis post hair transplantation, especially if an infection is present.
Pustules and Crust Formation
As the condition progresses, pustules may form, sometimes breaking open and creating crusts. This is a common sign of bacterial folliculitis.
Swelling and Redness
Localized swelling and redness around the follicular area indicate inflammation. While mild redness is common after a hair transplant, persistent redness can signal an ongoing folliculitis outbreak.
Scabbing or Scarring
In more severe cases, untreated folliculitis can lead to scabs or permanent scarring, affecting the aesthetic outcome of the hair transplant. Some people explore alternative care like home remedies and natural treatment to relieve minor symptoms at home. While these remedies are helpful, professional guidance is always recommended for post-transplant folliculitis.
Risk Factors for Folliculitis Post Hair Transplant
Certain conditions or behaviors can increase the likelihood of developing post hair transplant folliculitis:
- Pre-existing skin conditions: Individuals with acne or seborrheic dermatitis are more prone to folliculitis.
- Weakened immune system: Chronic illnesses or medications that suppress immunity can increase susceptibility.
- Poor hygiene: Not following post-operative care instructions can significantly raise the risk.
- Excessive sweating: Activities that make the scalp sweat heavily can contribute to follicle irritation.
- Use of irritants: Harsh shampoos, chemicals, or untested hair products applied too soon after the procedure can trigger inflammation.
Types of Folliculitis After Hair Transplant
Post-transplant folliculitis can present in different forms:
Superficial Folliculitis:
Affects only the upper part of the hair follicle. Usually mild and resolves within a few days with minimal intervention.
Deep Folliculitis:
Affects the entire follicle and may cause more pain and pus formation. This type can lead to scarring if left untreated.
Gram-Negative Folliculitis:
Less common, often associated with long-term antibiotic use. Can be more challenging to treat and requires medical attention.
Pseudofolliculitis:
Caused by hair curling back into the skin, more common in people with curly hair. Can result in small, painful bumps that mimic bacterial folliculitis. Herbal and supplementary treatments such as Fulical – highly effective herbal supplement for folliculitis are gaining popularity for patients seeking natural alternatives alongside conventional care.
Timeline of Folliculitis After Hair Transplant
Folliculitis may appear at different stages post-transplant:
- Immediate (0–2 weeks): Minor redness and bumps may appear as the scalp heals.
- Early (2–4 weeks): Infection-related folliculitis may develop if bacteria enter the scalp.
- Late (1–3 months): Persistent or severe folliculitis can indicate underlying issues like blocked follicles or poor hygiene.
Early recognition and treatment usually prevent complications and minimize the impact on hair growth.
Diagnosis of Folliculitis Post Hair Transplant
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Physical examination: Dermatologists inspect the scalp for characteristic bumps, redness, and inflammation.
- Medical history review: Information about recent procedures, medications, and skin conditions helps determine the cause.
- Laboratory tests: In some cases, bacterial cultures or skin swabs are performed to identify the exact pathogen.
For minor cases, patients sometimes try Natural treatment for folliculitis, but accurate diagnosis ensures proper management, especially after a surgical procedure.
Potential Complications
While most cases of folliculitis post hair transplant are mild, complications can occur:
- Scarring and permanent hair loss: Severe or untreated folliculitis can damage hair follicles permanently.
- Spread of infection: Infection can extend to nearby follicles, worsening symptoms.
- Delayed healing: Folliculitis can slow the overall recovery process after hair transplantation.
Patients often combine treatments with lifestyle measures and explore remedies or herbal supplements. Proper guidance ensures safety and efficacy.
When to See a Doctor
Immediate consultation is recommended if you notice:
- Increasing pain or redness
- Persistent pustules
- Swelling spreading beyond the transplant area
- Signs of systemic infection (fever, chills)
Early intervention can prevent scarring and ensure that your hair transplant results are not compromised.
Prevention Tips
Although this article focuses on understanding the disease, it is worth noting:
- Keep the scalp clean and dry
- Avoid scratching or picking at bumps
- Follow your surgeon’s post-transplant instructions carefully
- Use gentle, non-irritating hair products
Some people also consider alternative approaches like natural home remedies for folliculitis treatment at the later stage to support recovery.
Final Thoughts
Folliculitis post hair transplant is a common, generally temporary condition that arises due to follicle irritation or infection. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and risk factors is critical for effective management. While mild cases often resolve with proper care, severe cases can lead to scarring and hair loss.
Patients should monitor their scalp closely after transplantation, maintain hygiene, and seek professional care if symptoms persist. Natural remedies and herbal supplements can complement treatment but should not replace medical advice. Awareness and timely action ensure that hair transplant results remain successful and aesthetically pleasing.