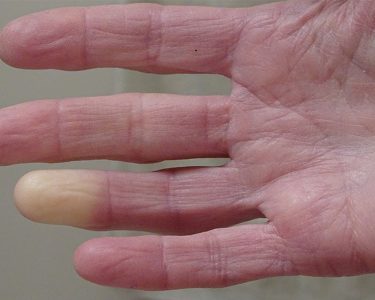
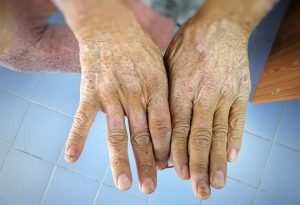
Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis) is an autoimmune connective tissue disease characterized by excessive collagen formation, skin tightening, and potential involvement of internal organs and vasculature. Conventional treatments—such as immunosuppressants and vasodilators—focus on symptom control but often fall short of addressing underlying fibrosis. As a result, both patients and clinicians have shown growing interest in natural adjuncts, including herbal supplements.
One such product, “CLEMICAL,” is marketed by Herbal Care Products for scleroderma support. In this review, we examine the science behind its ingredients, reported Uses and Benefits, and how it aligns with current evidence in natural therapies.
Product Overview: Clemical Herbal Supplement
Claims and Composition
Clemical is branded as a 100% natural tablet intended to:
- Soften hardened skin patches
- Relieve joint pain, dry cough, and gastrointestinal distress
- Improve circulation and organ function
- Offer an overall boost in energy and immunity
According to the product description, it works best when taken as two tablets daily after breakfast, with results expected within 30–35 days.
Ingredients in Clemical
Key active components include:
- Fevernut (Mucuna pruriens?)
- Rhubarb
- Indian Long Pepper (Piper longum)
- Calcium sulphate
- Gulancha (Clerodendrum spp.?)
While exact dosages are proprietary, these botanicals are traditionally used for anti-inflammatory, digestive, and circulation support.
Uses and Benefits
1. Skin Softening & Tissue Healing
Clemical claims to soften hardened, thickened skin—an effect often sought in localized scleroderma. Anecdotal reports mention softened patches and reduced skin tightness. Herbal ingredients like rhubarb and long pepper are historically thought to have anti-fibrotic and tissue-healing properties, though clinical trials in scleroderma are limited.
In contrast, phytochemicals such as EGCG from green tea and gotu kola (Centella asiatica) have demonstrated evidence in supporting skin quality and reducing fibrosis.
2. Joint Pain & Mobility Improvement
Joint discomfort is common in scleroderma. Clemical lists relief from wrist and joint pain as a key benefit. Traditional herbs like Piper longum show anti-inflammatory effects and may assist in musculoskeletal support. Meanwhile, natural agents such as gamma-linolenic acid and N-acetylcysteine (NAC) have shown benefit in reducing joint pain and Raynaud’s-related issues .
3. Enhanced Circulation & Raynaud’s Support
Poor circulation and vasospasm (Raynaud’s phenomenon) are hallmark issues. Clemical purports to promote blood flow and organ function. Evidence for supplements like evening primrose oil and green tea extract indicates improved microvascular health, a mechanism that might parallel Clemical’s theoretical effects .
4. Gastrointestinal Comfort
Scleroderma can affect esophageal motility and bowel function, causing reflux, constipation, or diarrhea. Users of Clemical have reported improved digestive symptoms, including reduced reflux, diarrhea control, and easier swallowing. Botanicals like rhubarb and long pepper are known to influence digestive dynamics, which may support these claims.
5. Immune & Energy Support
Clemical also claims to “boost immunity,” “fight germs,” and enhance cellular energy. While evidence is not directly cited, many botanicals in its formula are used traditionally to support metabolic and immune health. Scientific reviews have noted potential anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of herbs like turmeric, green tea, Centella asiatica, and others .
Scientific & Nutritional Context
Clinical Herbs in Scleroderma
- Centella asiatica has shown anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic effects, and wound healing benefits in small studies.
- Curcumin, green tea EGCG, and vitamins D/E are among botanical and micronutrient agents under investigation for fibrotic and vascular modulation.
Lifestyle & Diet
Standard recommendations emphasize antioxidant-rich foods (fruit, vegetables), anti-inflammatory spices (turmeric, ginger), and supplementation with vitamin D, E, NAC, and primrose oil .
Usage Directions & Safety
Clemical is advised at two tablets daily after breakfast, avoiding cold drinks and foods simultaneously. This scheduling aligns with traditional herbal protocols minimizing digestive disruption.
Precautions:
- As with all supplements, potential herb–drug interactions are possible (e.g., with blood thinners, immunosuppressants).
- Lack of regulated dosage and clinical trials means efficacy remains largely anecdotal.
- Users should consult their healthcare provider before introducing Clemical.
Comparative Perspective
Clemical aims to deliver multiple benefits under one supplement. From available data:
- Its skin-soothing and joint-relief claims align with patient priorities in scleroderma management.
- Similar herbal agents (Centella asiatica, green tea) have some clinical support.
- Other targeted supplements (e.g., NAC, GLA, vitamin D/E) are more extensively studied in scleroderma populations.
While Clemical: Herbal Treatment For Scleroderma offers an integrative approach, it lacks peer-reviewed trials. It may serve as a complementary therapy rather than a substitute for current standards.
Real-World Feedback
Customer testimonials shared on the site include reports of softened skin, less pain, better GI function, and improved energy within a 30–35 day window. Though encouraging, these anecdotal accounts should be interpreted with caution due to placebo effects and lack of formal monitoring.
Summary Table: Uses and Benefits
| Use Case | Clemical Claims | Corroborating Evidence |
| Skin softening | Softens hardened patches; controls scarring | Centella, EGCG, curcumin show antifibrotic effects |
| Joint pain relief | Reduces wrist/joint pain | GLA, NAC, Piper extracts have anti-inflammatory support |
| Improved circulation | Boosts blood flow; supports organ health | Primrose oil, EGCG improve vascular function |
| Digestive support | Alleviates reflux, diarrhea, swallowing issues | Piper, rhubarb used traditionally for GI motility |
| Immune & energy boost | “Fights germs,” energizes cells | Antioxidant and adaptogenic herbs have some supportive data |
Recommendations & Final Thoughts
- Consult First: Always speak with a rheumatologist or integrative medicine specialist before starting Clemical or similar supplements, especially when on prescription treatments or dealing with organ involvement.
- Make it Part of a Plan: Herbal supplements should complement—not replace—evidence-based therapies. Lifestyle changes like diet, exercise, and sun protection are essential.
- Monitor Effects: Track symptoms over 4–6 weeks to assess impact on skin, joints, digestion, and energy. Discontinue if adverse reactions emerge.
- Quality & Source: Choose products with transparent sourcing, ingredient verification, and good manufacturing practices.
Conclusion
Clemical Herbal Supplement for Scleroderma is positioned as a holistic support option for scleroderma, targeting skin fibrosis, joint discomfort, vascular health, and gastrointestinal symptoms. Its traditional herbal formula aligns with some scientifically grounded interventions, though it currently lacks clinical trial validation.
Its Uses and Benefits may offer valuable adjunctive support—particularly for symptom relief—especially when integrated within a broader natural health regimen. However, definitive conclusions await rigorous studies. For individuals with scleroderma seeking integrative approaches, measuring tolerability, tracking outcomes, and maintaining open communication with healthcare professionals are key.